Pneumonia, a common respiratory infection, can cause fluid buildup in the lungs, leading to breathing difficulties and discomfort. Fortunately, there are several effective ways to remove this fluid safely, aiding in recovery and restoring lung function. In this guide, we will delve into the methods healthcare professionals use to alleviate pneumonia-related lung fluid and provide essential tips for a smoother recovery.
Understanding Pneumonia and Lung Fluid Accumulation:
Pneumonia is an infection that inflames air sacs in one or both lungs, which may fill with fluid or pus, causing cough with phlegm or pus, fever, chills, and difficulty breathing. The severity of pneumonia varies, ranging from mild to life-threatening, depending on factors such as the type of germ causing the infection, overall health, and age.
Fluid accumulation in the lungs, known as pulmonary edema, is a common complication of pneumonia. When the air sacs in the lungs fill with fluid, it interferes with the ability to breathe and oxygenate the blood properly. Prompt and effective treatment is crucial to remove this fluid and prevent further complications.
Medical Interventions for Fluid Removal:
Healthcare providers employ various strategies to remove fluid from the lungs caused by pneumonia, tailored to the patient’s condition and the severity of the infection. Here are some common methods:
- Diuretics: Diuretics, also known as water pills, are medications that help the kidneys remove excess fluid from the body through urine. They are often prescribed to individuals with pneumonia-related fluid buildup to reduce swelling and improve breathing. However, diuretics should be used with caution, as they can cause electrolyte imbalances and other side effects.
- Oxygen Therapy: In cases where pneumonia severely compromises lung function, supplemental oxygen may be necessary to ensure the body receives an adequate oxygen supply. Oxygen therapy can improve oxygenation levels in the blood and alleviate symptoms such as shortness of breath and fatigue.
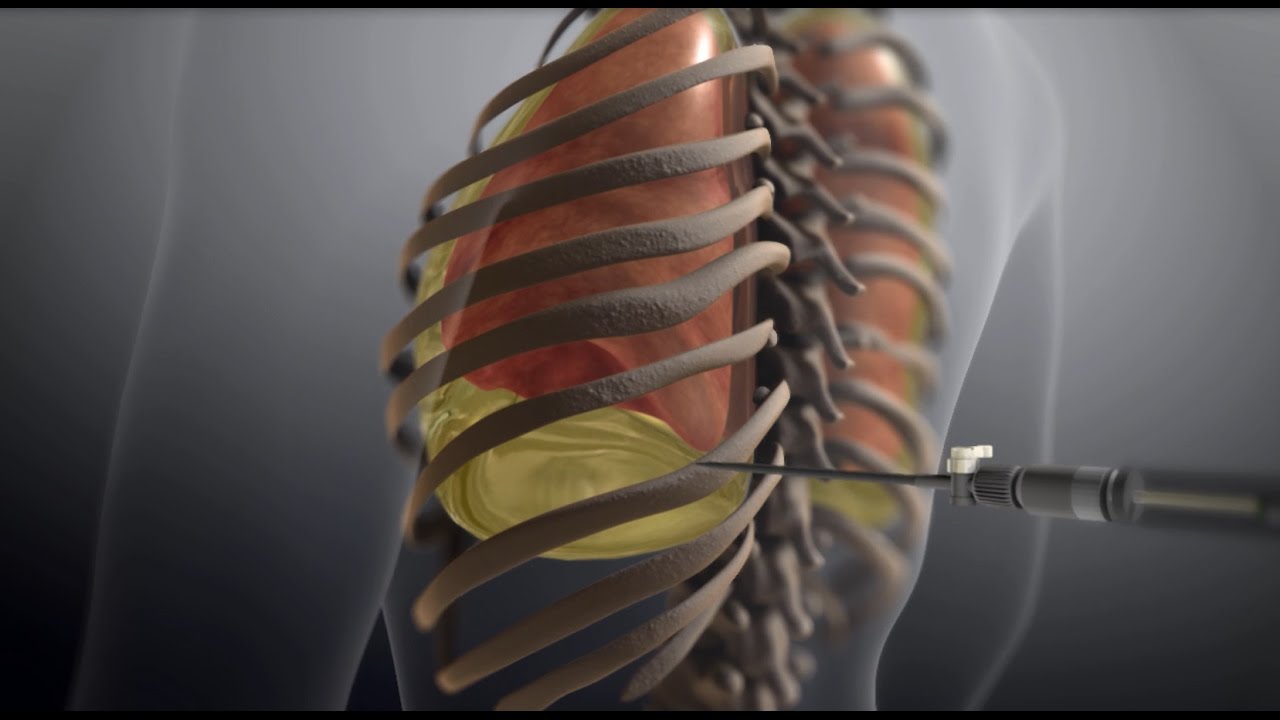
- Thoracentesis: Thoracentesis is a procedure in which a needle is inserted through the chest wall into the pleural space – the area between the lungs and the chest wall – to drain excess fluid. This technique can provide rapid relief for individuals with significant fluid accumulation and may be performed in a hospital or outpatient setting under local anesthesia.
- Mechanical Ventilation: In severe cases of pneumonia where respiratory failure occurs, mechanical ventilation may be required. This involves using a machine to assist with breathing or taking over the breathing process entirely. Mechanical ventilation can provide life-saving support for individuals struggling to breathe due to pneumonia-related lung fluid.
- Antibiotics: While not directly aimed at removing fluid from the lungs, antibiotics are essential for treating pneumonia caused by bacterial infections. By targeting the underlying cause of the infection, antibiotics help reduce inflammation and fluid buildup, allowing the lungs to heal more effectively.
- Chest Physiotherapy: Chest physiotherapy techniques, such as postural drainage, percussion, and vibration, can help loosen and mobilize mucus in the lungs, making it easier to cough up and expel. This can be particularly beneficial for individuals with pneumonia who are experiencing difficulty clearing secretions from their airways.
Recovery and Prevention Strategies:
In addition to medical interventions, several self-care measures can aid in the removal of fluid from the lungs and promote a speedier recovery from pneumonia:
- Stay Hydrated: Drinking plenty of fluids helps thin mucus secretions in the lungs, making them easier to expel through coughing. Aim to consume at least eight glasses of water per day, unless advised otherwise by your healthcare provider.
- Practice Deep Breathing Exercises: Deep breathing exercises can help expand the lungs and improve ventilation, facilitating the removal of fluid and mucus. Try inhaling deeply through your nose, holding your breath for a few seconds, and then exhaling slowly through your mouth.
- Use a Humidifier: Using a humidifier or steam inhalation can help moisturize the airways and loosen mucus, making it easier to cough up. Be sure to clean your humidifier regularly to prevent the growth of mold and bacteria.
- Avoid Smoking and Airborne Irritants: Smoking and exposure to airborne irritants such as pollution and strong chemicals can exacerbate lung inflammation and worsen symptoms of pneumonia. If you smoke, quitting is essential for promoting lung health and reducing the risk of complications.
- Follow Your Treatment Plan: It’s crucial to adhere to your prescribed treatment plan, including taking medications as directed and attending follow-up appointments with your healthcare provider. Skipping doses or neglecting medical advice can hinder recovery and increase the likelihood of complications.
Conclusion:
Pneumonia-related fluid buildup in the lungs presents formidable challenges to respiratory function and overall well-being. Yet, with swift medical intervention, attentive supportive care, and prudent lifestyle adjustments, the effective removal of fluid from the lungs and facilitation of pneumonia recovery become achievable goals. By acquainting oneself with the array of treatment options at hand and embracing proactive measures to nurture lung health, individuals can assert control over their recovery journey, ultimately experiencing a breath of relief. Should you or a loved one encounter symptoms of pneumonia, it is imperative to promptly seek medical attention, ensuring a timely diagnosis and treatment. Your lungs will express their gratitude. Additionally, when considering treatment options, consulting the best chest surgeon in India can offer unparalleled expertise and guidance for optimal recovery.